Envelopes
Contents
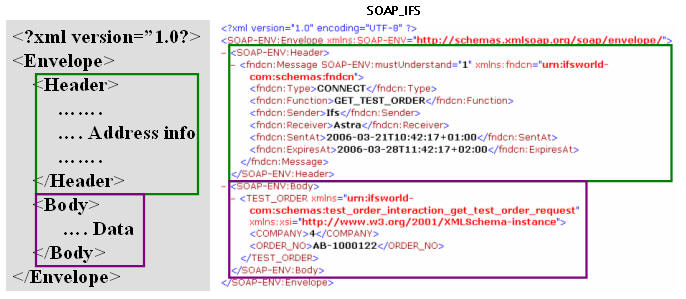
An envelope normally consists of two parts:
- A Header containing address data, properties and other
information about the message.
- A Body that contains the message data.
IFS Connect has support for plugging in envelopes (XML Envelope Definitions).
As part of a standard installation are SOAP_SIMPLE and
SOAP_IFS.
XML Envelope Definitions are used for
- Format of the outbound message
- Recognize of inbound messages
- Format of the response (when synchronous request/response)
- Format of the error response
XML Envelope Definitions are stored in the database in form of XML files and
they are administered in the
Connect
configuration tool.
Note: If other envelopes then SOAP_IFS and SOAP_SIMPLE is needed then
read:
Customization of
envelopes
Envelopes are used to encapsulate xml data. A definition file in xml format is used as
the envelope definition.
Envelopes are stored in the database and are defined using the Connect Configuration tool
feature.
They are connected
to an address in
Message Routing rules.
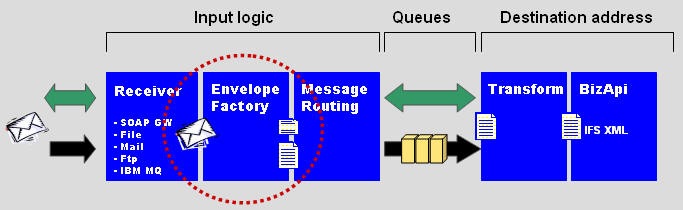
- A message is received by some Reader in IFS Connect.
The Reader is just a protocol implementation and will not change the
message.
- The Envelope Factory tryes to recognize which Envelope it is.
It will use all the XML Envelope Definitions that is stored in the IFS
database.
In a standard installation SOAP_IFS and SOAP_SIMPLE are
stored.
If not the input message is recognized as a known envelope it will
classified as:
UNKNOWN_XML: if xml format
NONE_XML: if none xml format
- The Envelope Factory splits up the message into two parts:
A Header that will be used as Content Based routing parameters. This
parameters is predefined.
A Body that contains the data. This will be passed forward to the
Transformer Factory.
For UNKNOWN_XML and NONE_XML will header and body be the same and contain
the whole message.
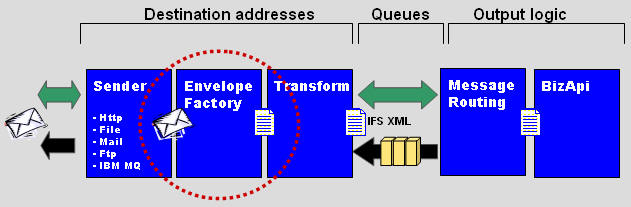
- An outbound message in IFS XML format is transformed to any format by
the Transformer Factory.
- The destination address in the
Message Routing determines which Envelope should be used for
carrying the data. If no Envelope is specified then will the data be sent as
it is. (sent as a letter without envelope)
- The message will be delivered to it's destination by a Sender.
The Sender is just a protocol implementation and will not change the
message.



